Getting Started
Welcome to the official documentation for the Quality Management System (QMS). This guide will help you navigate every aspect of the platform — from installation and configuration to ongoing management and workflow automation. You’ll find step-by-step instructions to set up modules, define workflows, manage access permissions, automate reminders, and maintain compliance across your organization.
Whether you’re a System Administrator, Compliance Officer, Auditor, or End User, this documentation serves as your go-to resource for installing, configuring, maintaining, and scaling the QMS efficiently and securely.
🌐 Overview
The QMS is a comprehensive, modular platform built to help organizations streamline, standardize, and automate their quality processes. It ensures compliance with internal policies and external standards (such as ISO, GDPR, and industry regulations) through a centralized and intelligent workflow ecosystem.
- Audit Management – Plan, execute, and track audits with precision.
- CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Action) – Identify, document, and resolve issues effectively.
- Non-Conformance Handling – Capture and manage deviations from standards.
- Risk Management – Assess and mitigate potential quality risks.
- Complaint Management – Efficiently resolve customer or supplier concerns.
- Training Module – Track employee competencies and certifications.
- Document Management – Organize, approve, and sign controlled documents.
- Automated Reminders & Notifications – Stay ahead of reviews, audits, and renewals.
- Access Control – Define dynamic, role-based permissions across modules.
- Workflow Automation – Define custom approval and review processes.
- Logs & Dashboards – Real-time visibility, analytics, and traceability.
⚙️ Core Capabilities
The QMS platform integrates intelligent automation, cloud scalability, and compliance-driven features to improve transparency and productivity across your organization.
- Dynamic Role-Based Access Control: Define granular permissions and assign roles dynamically across modules.
- Automated Workflow Engine: Create multi-step workflows for approvals, CAPAs, or audits.
- Integrated Document Management: Manage controlled documents with signatures, versioning, and retention policies.
- Risk & Compliance Monitoring: Continuously evaluate risks linked to CAPA or audit activities.
- Comprehensive Dashboard: View real-time analytics on audits, CAPAs, and document statuses.
- Automated Reminders: Schedule recurring or one-time reminders to ensure timely completion of tasks.
- Cloud & On-Premise Flexibility: Supports deployment with Amazon S3 or local file storage.
🚀 Getting Started
- Install & Configure: Set up backend, frontend, database, and storage.
- Set Up Roles & Access: Define Admins, Managers, and Auditors with dynamic permissions.
- Create Workflows: Design your first approval or audit workflow in the Workflow Module.
- Upload Documents: Manage SOPs and policy manuals through the Document Management Module.
- Enable Notifications: Activate reminders and alerts for audits and renewals.
- Start Quality Cycles: Launch audits or CAPAs to simulate real process flow.
- Monitor Dashboards: Track activity, progress, and compliance in real-time.
🔒 Why Choose the QMS?
- Centralized management of all quality and compliance processes.
- Automation of manual, repetitive tasks to reduce administrative effort.
- Scalable, secure, and auditable infrastructure.
- Seamless collaboration between teams, departments, and suppliers.
Requirements
Before installing Quality Management System, ensure that your server meets the following requirements:
- .NET 8.0 Runtime or SDK
- Microsoft SQL Server or SQL Server Express or MySQL
- IIS 10.0+ (Windows) or Nginx/Apache (Linux)
- Windows Server or Linux (Ubuntu 20.04+, CentOS 8+)
- Minimum 4GB RAM (8GB recommended)
🪟 IIS Installation (Windows Server)
Prerequisites for IIS
- Windows Server 2019 or later / Windows 10/11
- IIS 10.0 or later
- .NET 8 Hosting Bundle
- SQL Server or SQL Server Express
Step 1: Install .NET 8 Hosting Bundle
- Download the .NET 8 Hosting Bundle from Microsoft's official website
- Run the installer as Administrator
- Restart IIS after installation:
iisreset
Step 2: Enable IIS Features
Open PowerShell as Administrator and run:
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName IIS-WebServerRole, IIS-WebServer, IIS-CommonHttpFeatures, IIS-HttpErrors, IIS-HttpRedirect, IIS-ApplicationDevelopment, IIS-NetFxExtensibility45, IIS-HealthAndDiagnostics, IIS-HttpLogging, IIS-Security, IIS-RequestFiltering, IIS-Performance, IIS-WebServerManagementTools, IIS-ManagementConsole, IIS-IIS6ManagementCompatibility, IIS-Metabase, IIS-ASPNET45Step 3: Create Application Pool
- Open IIS Manager
- Right-click Application Pools → Add Application Pool
- Name:
QMS_Pool - .NET CLR Version: No Managed Code
- Managed Pipeline Mode: Integrated
- Click OK
- Right-click the new pool → Advanced Settings
- Set Identity to ApplicationPoolIdentity
- Set Load User Profile to True
Step 4: Deploy Application Files
- Extract the QMS application files to
C:\inetpub\wwwroot\QMS - Ensure the IIS_IUSRS group has read and execute permissions on the folder
- Grant full control to the application pool identity on the following folders:
- wwwroot
- Logs
- Temp
Step 5: Create Website in IIS
- Right-click Sites → Add Website
- Site name:
QMS - Application pool:
QMS_Pool - Physical path:
C:\inetpub\wwwroot\QMS - Binding: HTTP, Port 80 (or HTTPS 443 with SSL certificate)
- Host name:
qms.yourdomain.com
Step 6: Configure Database Connection
Edit the appsettings.json file in the application root:
{
"ConnectionStrings": {
"DefaultConnection": "server=localhost;port=3306;user=root;password='';database=qms_db;AllowPublicKeyRetrieval=True;SslMode=None;"
}
}✅ Final Configuration Steps
- Set up SSL Certificate:
Configure SSL/TLS certificates for HTTPS support using Let's Encrypt or commercial certificates
- Configure Firewall:
Open necessary ports (80, 443) and restrict access to the application port (5000) from external sources
- Set up Monitoring:
Configure application logging and monitoring for production environments
Tesseract OCR Installation for Window OS Server
- Download the Tesseract Installer:
Visit the official UB Mannheim GitHub page and download
👉 tesseract-ocr-w64-setup-v5.2.0.20220708.exe - Install Tesseract:
Run the installer and follow the prompts. During setup:- Select your language packs (at minimum, keep
engchecked for English). - Ensure the option to add Tesseract to the system PATH is selected.
- Select your language packs (at minimum, keep
- Verify PATH Configuration (if not set automatically):
- Go to System Properties → Advanced → Environment Variables.
- Under "System variables", select Path → click Edit.
- Add this path (if not already there):
C:\Program Files\Tesseract-OCR - Click OK to save and close all dialogs.
- Verify Installation:
Open Command Prompt and run:
You should see the installed version and copyright.tesseract -v - Application Setup:
Make sure your application has atessdatafolder placed inside thewwwrootdirectory.
Example path:C:\\inetpub\\wwwroot\\{{yoursitename}}\\wwwroot\\tessdata - Set Folder Permissions:
Grant full read/write permissions to the application pool identity or service user (IIS_IUSRS) running your web app:- Ensure read access to
tesseract.exe. - Ensure read/write access to the
C:\\inetpub\\wwwroot\\{{yoursitename}}\\tessdatafolder to user IIS_IUSRS. - If hosted on a shared/VPS platform, confirm additional restrictions with your provider.
- Ensure read access to
- Test Tesseract OCR:
To check if OCR works correctly, run this in the Command Prompt:tesseract path\to\image.png output-text-file -l eng- Replace
path\to\image.pngwith the actual image path. - The output will be saved as
output-text-file.txt.
- Replace
- Restart the IIS server
http://qms.yourdomain.com
and follow the initial setup wizard to configure the administrator account and basic application
settings.
🐧 Nginx Installation (Linux)
Prerequisites for Nginx
- Ubuntu 20.04+ / CentOS 8+ / RHEL 8+
- Nginx 1.18+
- .NET 8 Runtime
- SQL Server or MySQL
Step 1: Install .NET 8 Runtime
For Ubuntu/Debian:
wget https://packages.microsoft.com/config/ubuntu/20.04/packages-microsoft-prod.deb -O packages-microsoft-prod.deb
sudo dpkg -i packages-microsoft-prod.deb
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y aspnetcore-runtime-8.0For CentOS/RHEL:
sudo dnf install aspnetcore-runtime-8.0Step 2: Install and Configure Nginx
sudo apt update
sudo apt install nginx
sudo systemctl start nginx
sudo systemctl enable nginxStep 3: Deploy Application
- Create application directory:
sudo mkdir -p /var/www/qms - Extract application files to
/var/www/qms - Set proper permissions:
sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/qms sudo chmod -R 755 /var/www/qms sudo chmod -R 777 /var/www/qms/wwwroot sudo chmod -R 777 /var/www/qms/Logs sudo chmod -R 777 /var/www/qms/Temp
Step 4: Configure Nginx Virtual Host
Create /etc/nginx/sites-available/qms
server {
listen 80;
server_name qms.yourdomain.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:5000;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection keep-alive;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_cache_bypass $http_upgrade;
}
# Static files
location ~* \.(css|js|png|jpg|jpeg|gif|ico|svg)$ {
root /var/www/qms/wwwroot;
expires 1y;
add_header Cache-Control "public, immutable";
}
}Step 5: Enable Site and Test
sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/qms /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/
sudo nginx -t
sudo systemctl reload nginxStep 6: Create Systemd Service
Create /etc/systemd/system/qms.service
[Unit]
Description=QMS .NET Web API
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=notify
ExecStart=/usr/bin/dotnet /var/www/qms/QMS.dll
Restart=always
RestartSec=5
KillSignal=SIGINT
SyslogIdentifier=qms
User=www-data
Environment=ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT=Production
Environment=DOTNET_PRINT_TELEMETRY_MESSAGE=false
WorkingDirectory=/var/www/qms
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetEnable and start the service:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable qms.service
sudo systemctl start qms.service
sudo systemctl status qms.serviceTesseract OCR Installation for Linux
- Update your system:
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade - Install Tesseract OCR:
sudo apt install tesseract-ocr - Install languages (optional):
sudo apt install tesseract-ocr-eng sudo apt install tesseract-ocr-[lang] - Verify installation:
tesseract -v - Create
tessdatadirectory (if needed):mkdir -p /var/www/{{yoursitename}}/wwwroot/tessdata - Set permissions:
sudo chmod -R 755 /var/www/{{yoursitename}}/wwwroot/tessdata - Manual OCR Test (optional):
tesseract /path/to/image.png output-text -l eng - Install dependencies:
sudo apt-get install -y libtesseract-dev libleptonica-dev - Verify library files:
find /usr -name "libtesseract.so*" find /usr -name "libleptonica.so*" - Copy to x64 directory in project:
cp /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libtesseract.so* /var/www/{{yoursitename}}/x64/cp /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libleptonica.so* /var/www/{{yoursitename}}/x64/
or use/usr/local/lib/path if applicable. - Set
LD_LIBRARY_PATHglobally:
Or edit:export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/var/www/{{yoursitename}}/x64/ source ~/.bashrcsudo nano /etc/environment LD_LIBRARY_PATH="/var/www/{{yoursitename}}/x64/:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH" - Compatible Versions:
- Tesseract 5.2.0
- libtesseract 5.2.x
- libleptonica 1.82.0+
- Restart services:
sudo systemctl restart {{yoursitename}}.service sudo systemctl restart nginx
✅ Final Configuration Steps
- Set up SSL Certificate:
Configure SSL/TLS certificates for HTTPS support using Let's Encrypt or commercial certificates
- Configure Firewall:
Open necessary ports (80, 443) and restrict access to the application port (5000) from external sources
- Set up Monitoring:
Configure application logging and monitoring for production environments
http://qms.yourdomain.com
and follow the initial setup wizard to configure the administrator account and basic application
settings.
🔶 Apache Installation
Prerequisites for Apache
- Apache 2.4+
- .NET 8 Runtime
- mod_proxy and mod_proxy_http modules
- SQL Server or MySQL
Step 1: Install .NET 8 Runtime
Follow the same .NET installation steps as described in the Nginx section above.
Step 2: Install and Configure Apache
For Ubuntu/Debian:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install apache2
sudo a2enmod proxy
sudo a2enmod proxy_http
sudo a2enmod headers
sudo systemctl restart apache2Step 3: Deploy Application
Follow the same deployment steps as described in the Nginx section.
Step 4: Configure Apache Virtual Host
Create /etc/apache2/sites-available/qms.conf
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName qms.yourdomain.com
DocumentRoot /var/www/qms/wwwroot
ProxyPreserveHost On
ProxyPass /api/ http://localhost:5000/api/
ProxyPassReverse /api/ http://localhost:5000/api/
ProxyPass / http://localhost:5000/
ProxyPassReverse / http://localhost:5000/
# Headers for better proxy support
ProxyPassReverse / http://localhost:5000/
RequestHeader set X-Forwarded-Proto "http"
RequestHeader set X-Forwarded-Port "80"
# Static files handling
Alias /wwwroot /var/www/qms/wwwroot
<Directory "/var/www/qms/wwwroot">
AllowOverride None
Require all granted
</Directory>
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/qms_error.log
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/qms_access.log combined
</VirtualHost>Step 5: Enable Site and Restart Apache
sudo a2ensite qms.conf
sudo apache2ctl configtest
sudo systemctl reload apache2Step 6: Create Systemd Service
Use the same systemd service configuration as described in the Nginx section.
🗄️ Database Configuration
SQL Server Configuration
- Create a new database named
QMS_DB - Create a database user with appropriate permissions
- Update the connection string in
appsettings.json"ConnectionStrings": { "DefaultConnection": "server=localhost;port=3306;user=root;password='';database=qms_db;AllowPublicKeyRetrieval=True;SslMode=None;" }
MySQL Configuration (Alternative)
- Install MySQL server and create database
- Update connection string for MySQL:
"ConnectionStrings": { "DefaultConnection": "server=localhost;port=3306;user=root;password='';database=qms_db;AllowPublicKeyRetrieval=True;SslMode=None;" }
Tesseract OCR Installation for Linux
- Update your system:
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade - Install Tesseract OCR:
sudo apt install tesseract-ocr - Install languages (optional):
sudo apt install tesseract-ocr-eng sudo apt install tesseract-ocr-[lang] - Verify installation:
tesseract -v - Create
tessdatadirectory (if needed):mkdir -p /var/www/{{yoursitename}}/wwwroot/tessdata - Set permissions:
sudo chmod -R 755 /var/www/{{yoursitename}}/wwwroot/tessdata - Manual OCR Test (optional):
tesseract /path/to/image.png output-text -l eng - Install dependencies:
sudo apt-get install -y libtesseract-dev libleptonica-dev - Verify library files:
find /usr -name "libtesseract.so*" find /usr -name "libleptonica.so*" - Copy to x64 directory in project:
cp /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libtesseract.so* /var/www/{{yoursitename}}/x64/cp /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libleptonica.so* /var/www/{{yoursitename}}/x64/
or use/usr/local/lib/path if applicable. - Set
LD_LIBRARY_PATHglobally:
Or edit:export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/var/www/{{yoursitename}}/x64/ source ~/.bashrcsudo nano /etc/environment LD_LIBRARY_PATH="/var/www/{{yoursitename}}/x64/:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH" - Compatible Versions:
- Tesseract 5.2.0
- libtesseract 5.2.x
- libleptonica 1.82.0+
- Restart services:
sudo systemctl restart {{yoursitename}}.service sudo systemctl restart nginx
✅ Final Configuration Steps
- Set up SSL Certificate:
Configure SSL/TLS certificates for HTTPS support using Let's Encrypt or commercial certificates
- Configure Firewall:
Open necessary ports (80, 443) and restrict access to the application port (5000) from external sources
- Set up Monitoring:
Configure application logging and monitoring for production environments
http://qms.yourdomain.com
and follow the initial setup wizard to configure the administrator account and basic application
settings.
Activate License
To activate your Production license, please follow the instructions below:
- Please enter the purchase code from your CodeCanyon account for this item. Click here to find your purchase code.
- Click on the "Activate License" button below.
- Login with codecanyon purchase account or already login then click on approve.
- A token has been generated.
- The system will redirect you to the login page. Kindly login again to continue.
- Enjoy full access to all features of Pro QMS - Advanced Quality Management System.
- Important: After activating the production license for a specific domain or sub-domain, token regeneration for another domain or sub-domain will not be permitted.
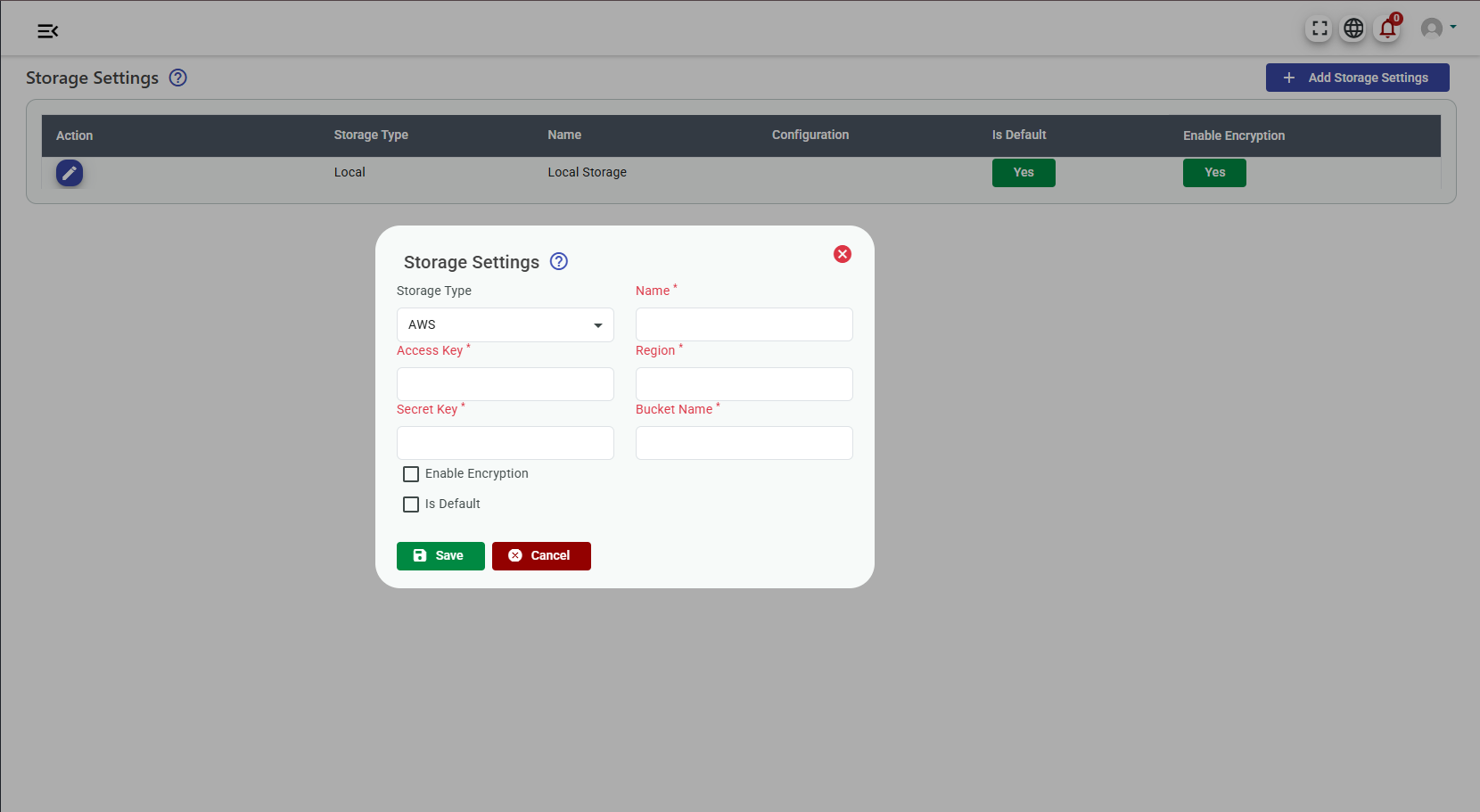
Storage Settings
We're excited to announce the latest upgrade to our Document Management system: seamless integration with Amazon S3 storage. With this new feature, users can now enjoy enhanced flexibility and reliability in storing their documents. By leveraging Amazon S3, one of the most trusted cloud storage solutions available, users can upload their documents with confidence, knowing that their data is securely stored and easily accessible whenever they need it. This integration opens up a world of possibilities for efficient document management, allowing users to take advantage of Amazon's scalable infrastructure to handle their growing document storage needs.
In order to configure the Amazon S3 storage, you will need to setup the S3 bucket, and then configure the Document Management System to use the Amazon S3 storage.
Configure Storage(Settings -> Storage Settings)
- Amazon S3 key
- Amazon S3 secret
- Amazon S3 region
- Amazon S3 bucket
SMTP User Manual
Welcome! This user manual provides a clear, step-by-step guide on how to configure Gmail and Microsoft SMTP for sending emails from your application. Following this guide ensures a secure and reliable email setup.
Gmail SMTP Configuration
Step 1: Enable 2-Step Verification
1. Open your Google Account Security page: https://myaccount.google.com/security
2. Under "Signing in to Google", enable 2-Step Verification (2FA).
3. Complete the setup using your mobile device. This step is required to generate a secure App Password for your application.
Step 2: Generate an App Password
1. After enabling 2FA, visit: https://myaccount.google.com/apppasswords
2. Configure the app password settings:
- App: Mail
- Device: Other (Custom Name) → enter a descriptive name like
MyApp SMTP
3. Click Generate and copy the 16-character password displayed. Example:
abcd efgh ijkl mnop
This App Password will be used instead of your normal Gmail password for your application.
Step 3: Gmail SMTP Settings
Use the following SMTP settings in your backend application (Laravel, .NET, Node.js, etc.):
| SMTP Host | smtp.gmail.com |
| SMTP Port | 587 (TLS) or 465 (SSL) |
| Encryption | TLS or SSL |
| Username | Your full Gmail address (e.g., [email protected]) |
| Password | The App Password you generated (not your Gmail password) |
| From Email | Your Gmail address |
| From Name | Your desired sender name |
After configuring these settings, your application should be able to send emails securely using Gmail SMTP.
Microsoft SMTP Configuration
This guide explains how to configure your Microsoft (Outlook / Office 365) account to send emails from your application securely. Please follow these steps carefully to ensure a successful setup.
Step 1: Check Account Type and Permissions
Microsoft accounts require proper authentication to send emails via SMTP. Please ensure:
- Your account is either personal Outlook or Office 365 / Microsoft 365.
- You have access to the account's security settings.
- Your account is allowed to use SMTP (for Office 365, the admin may need to enable SMTP AUTH).
Step 2: Decide Authentication Method
There are two ways to authenticate when sending emails:
- App Password (Legacy / Personal Accounts): Works only if 2FA is enabled and your account allows app passwords.
- OAuth2 / Modern Authentication: Recommended for Office 365 or business accounts; secure and compliant with Microsoft policies.
Step 3: Microsoft SMTP Settings
Use the following SMTP settings in your application backend (Laravel, .NET, Node, etc.):
| SMTP Host | smtp.office365.com |
| SMTP Port | 587 (TLS) or 465 (SSL) |
| Encryption | TLS / SSL |
| Username | Your Microsoft email address (e.g., [email protected]) |
| Password / Access Token |
|
| From Email | Your Microsoft email address |
| From Name | Your desired sender name |
Step 4: Test Your Configuration
Once SMTP is configured, test sending an email from your application to ensure everything is working correctly. Check the inbox and spam folder to confirm delivery.
Step 5: Troubleshooting
- If email fails, check that SMTP AUTH is enabled for your account.
- Verify your firewall or hosting provider is not blocking port 587/465.
- For OAuth2, ensure your token is valid and hasn’t expired.
Open AI Settings
Configure Storage(Settings -> General Settings -> Open AI API Key)
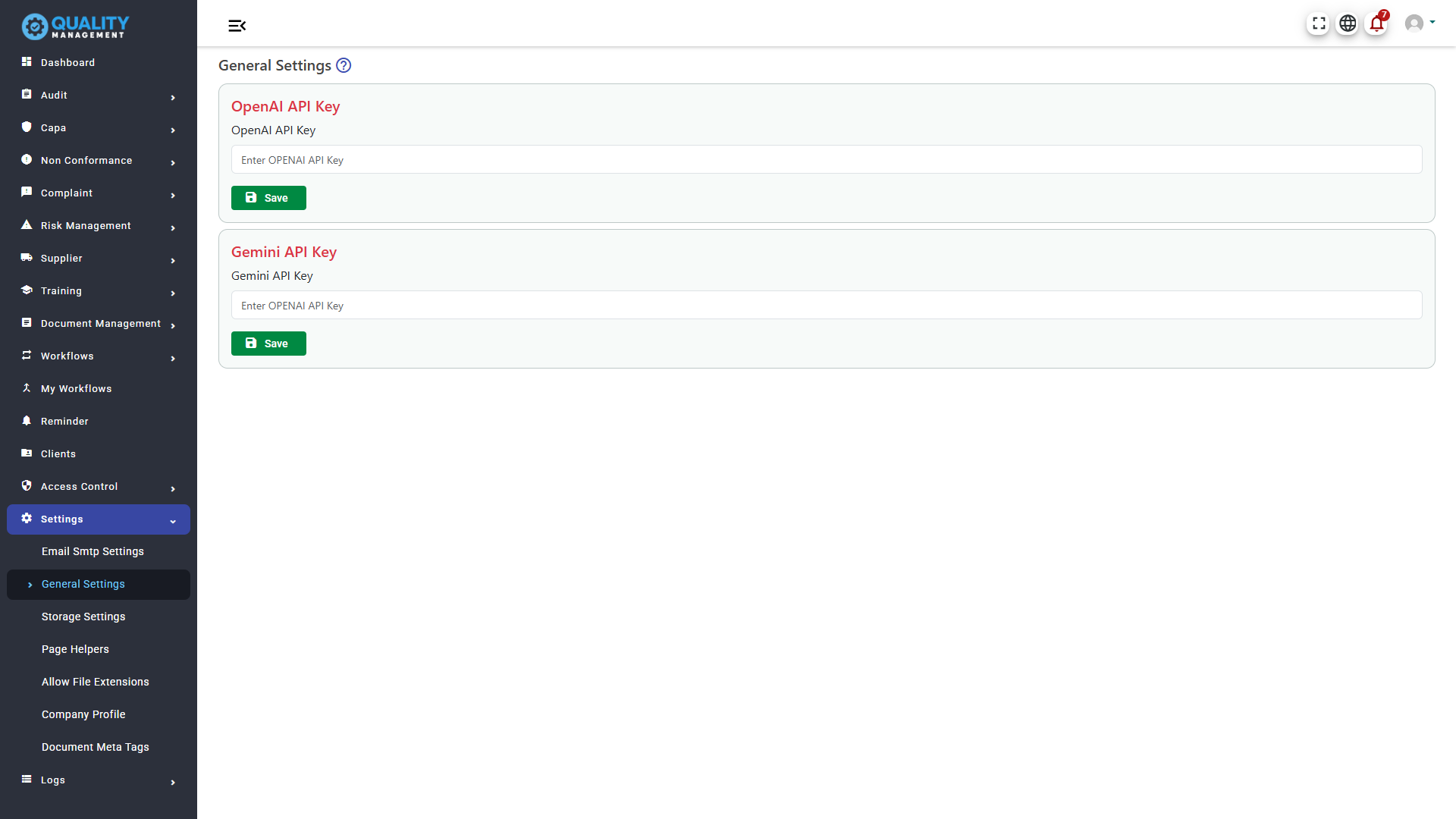
Google Gemini Settings
Configure Storage(Settings -> General Settings -> Google Gemini API Key)

Troubleshooting
PDF preview
Failed to load module script: Expected a JavaScript module script but the server responded with a MIME type of "application/octet-stream". Strict MIME type checking is enforced for module scripts per HTML spec.
This error is caused by the server not serving the PDF file with the correct MIME type. To fix this issue, you will need to add the following code to your server configuration file.
IIS (web.config):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<configuration>
<system.webServer>
<staticContent>
<mimeMap fileExtension=".mjs" mimeType="text/javascript" />
<mimeMap fileExtension=".ftl" mimeType="text/plain" />
</staticContent>
</system.webServer>
</configuration>
NGINX requires this configuration:
http {
...
types {
text/javascript mjs;
text/plain ftl;
text/javascript js;
}
}
APPACHE requires this configuration:
.htaccess file or extend your Apache config file with the following htaccess
<IfModule mod_mime.c> AddType text/javascript mjs AddType text/plain ftl </IfModule>
AWS amplify requires this configuration in the amplify.yaml file:
customHeaders:
- pattern: '*.mjs'
headers:
- key: 'Content-Type'
value: 'application/javascript'
- pattern: '*.ftl'
headers:
- key: 'Content-Type'
value: 'text/plain'
Apache Logs
Apache errors (including permission errors or misconfigured virtual hosts) are typically found in:
/var/log/apache2/error.log
Ensure mod_rewrite is enabled and your virtual host configuration allows overriding with
`.htaccess`.
Nginx Logs
Nginx error logs (useful for Laravel routing or permission issues) are located at:
/var/log/nginx/error.log
Make sure your Nginx server block (site config) points to the /public folder and the
correct PHP version is referenced in the fastcgi_pass
Angular Development Errors
When developing the frontend (Angular), open your browser’s developer console (F12) to see errors and warnings. These usually help with:
- Missing modules or dependencies
- API request errors (check network tab)
- Routing or component loading issues
If errors occur during development build, run:
npm install
npm start
Run Project Locally
Installation .NET REST API in Local System steps
- Open solution file QualityManagement.sln from .Net folder into visual studio 2022.
- Right click on solution explorer and Restore nuget packages.
- Change database connection string in appsettings.Development.json in QualityManagement.API project.
- Open package manager console from visual studio menu --> Tools --> nuget Package Manager --> Package Manager Console
- In package manager console, Select default project as QualityManagement.Domain
- Run Update-Database command in package manager console which create database and insert intial data.
- From Solution Explorer, Right click on QualityManagement.API project and click on Set as Startup Project from menu.
- To run project Press F5.
Angular Local System
- To run a local copy in development mode, replace REST API URI (apiUrl) variable in environment file inside src --> environments -->environment.ts
- opens a terminal
- run npm install -f command
- run npm start command. which will runs the UI at http://localhost:4200/
Audit
The Audit Module enables organizations to plan, execute, review, and close audits for departments, processes, and suppliers. It provides structured checklists, evidence capture, reviewer workflows, and integration with corrective actions to ensure compliance and continuous improvement.
Core Functions
- Audit Planning & Scheduling — Create audit plans, set frequency, scope and assign auditors.
- Audit Execution — Use templates/checklists to record observations and attach evidence.
- Findings & Non-Conformance — Log non-conformities and link them to follow-up actions.
- Review & Approval — Submit reports for reviewer validation and approval.
- Reporting & Analytics — Generate audit reports and view trends and compliance dashboards.
- Follow-up & Closure — Monitor CAPA and NC closure; close audits when all actions are complete.
Workflow / Process Flow
Step-by-step
- Create Audit Plan — Define type, scope, auditors and schedule.
- Assign & Notify — System sends notifications to assigned auditors.
- Conduct Audit — Auditor completes checklist, records evidence and findings.
- Raise Non-Conformance — For NCs, create linked records and optionally generate CAPA.
- Submit for Review — Reviewer validates and approves or requests revisions.
- Track Follow-up — Monitor related CAPA/NC until verified complete.
- Close Audit — Finalize report; archive and include in analytics.
Quick ASCII Diagram
Create Audit Plan
↓
Assign Auditor(s) → Notify
↓
Conduct Audit → Record Findings & Upload Evidence
↓
Create Non-Conformance (if any) → Auto-Link to CAPA
↓
Submit for Review
↓
Review & Approve Audit
↓
Monitor CAPA / NC → Automated Reminders
↓
Close Audit → Generate Report
Example Use Case
Scenario: A Quality Manager schedules a quarterly internal audit for Production. An Auditor performs the audit, finds two minor non-conformities and uploads photos. The system creates linked non-conformance records and CAPA requests. Department Head reviews and marks CAPAs complete; the audit is closed and dashboard reflects the completion.
Example Roles & Responsibilities (Illustrative)
| Role (example) | Responsibility |
|---|---|
| Administrator | Setup templates, configure workflows and assign permissions. |
| Quality Manager | Create audit plans, assign auditors, review and close audits. |
| Auditor | Conduct audits, record findings and evidence. |
| Reviewer / Department Head | Validate results and ensure corrective actions are implemented. |
| Employee (Auditee) | Provide information and implement assigned actions. |
Key Benefits
- End-to-end audit traceability (plan → findings → CAPA → closure)
- Documented evidence and attachments for regulatory compliance
- Actionable reports and dashboards for continuous improvement
- Dynamic role-based access ensures least-privilege principles
CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Action)
The CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Action) Module helps identify, investigate, and resolve the root causes of non-conformities or audit findings. It ensures that both corrective and preventive actions are systematically planned, executed, verified, and documented. The CAPA module is central to the continuous improvement process of the QMS.
Core Functions
- CAPA Initiation — Create CAPA records manually or automatically from non-conformances or audit findings.
- Root Cause Analysis — Document detailed analysis using methodologies such as 5 Whys or Fishbone Diagram.
- Action Planning — Define corrective and preventive actions, assign responsibilities, and set target dates.
- Implementation Tracking — Monitor progress and ensure completion of assigned actions.
- Effectiveness Verification — Review and verify if implemented actions resolved the root cause.
- Closure — Approve and close CAPA once verified effective.
Workflow / Process Flow
Step-by-step
- CAPA Initiation — Triggered automatically from a Non-Conformance or Audit Finding, or manually created by authorized users.
- Investigation & Root Cause Analysis — Responsible users document root cause using selected methodology.
- Action Planning — Define and assign Corrective Actions (CA) and Preventive Actions (PA) with deadlines.
- Implementation — Assigned users execute actions; progress tracked via reminders and dashboards.
- Verification & Review — Reviewer validates if the root cause was effectively addressed.
- CAPA Closure — CAPA marked as closed after review approval and documentation of results.
Quick ASCII Diagram
Non-Conformance / Audit Finding
↓
CAPA Initiation → Assign Responsible Person
↓
Root Cause Analysis → Define Corrective & Preventive Actions
↓
Action Implementation → Track via Reminders
↓
Effectiveness Verification → Reviewer Approval
↓
CAPA Closure → Generate Report
Example Use Case
Scenario: During an internal audit, a recurring documentation error is found. A CAPA is automatically created. The Quality Engineer identifies the root cause as insufficient training, defines corrective action (retraining staff), and preventive action (updating documentation process). After implementation and verification, the CAPA is closed, ensuring process reliability.
Example Roles & Responsibilities (Illustrative)
| Role (example) | Responsibility |
|---|---|
| Administrator | Configures CAPA categories, templates, and permissions. |
| Quality Manager | Initiates CAPA, assigns responsibilities, and approves closure. |
| Investigator / Engineer | Conducts root cause analysis and defines corrective/preventive actions. |
| Responsible User | Implements assigned actions and provides evidence of completion. |
| Reviewer | Validates CAPA effectiveness and approves closure. |
Key Benefits
- Ensures systematic problem-solving and prevention of recurrence.
- Centralized tracking of corrective and preventive actions.
- Audit trail and documentation enhance compliance readiness.
- Dynamic role-based access ensures flexibility and security.
Non-Conformance (NC)
The Non-Conformance (NC) Module of the QMS system enables organizations to identify, record, track, and resolve non-conformances across processes, products, and supplier activities. It ensures that all non-compliances are properly investigated, assigned corrective actions, and closed following verification by the quality team. The goal is to ensure continuous improvement and compliance with internal and external quality standards.
Key Objectives
- Provide a centralized system for recording and monitoring non-conformances.
- Facilitate root cause analysis and CAPA initiation.
- Maintain traceability of actions and accountability across roles.
- Enable real-time tracking for overdue NCs.
- Generate analytical insights to prevent recurrence of issues.
Core Functionalities
- NC Creation: Authorized users can log new NC records with information such as category, process area, description, severity, source, and evidence attachments.
- Assignment: The NC is assigned to a responsible investigator or department.
- Action Linking: Create and link CAPA requests to ensure follow-up corrective and preventive measures are implemented.
- Verification: Quality Managers verify the implementation and effectiveness of actions taken.
- Closure: Once verified, the NC is formally closed and archived for future reference.
Workflow
Step 1: Identification → User identifies and records a non-conformance.
Step 2: Review → Quality Manager reviews details and assigns it to a
responsible person.
Step 3: Investigation → The assigned person performs root cause analysis and
proposes actions.
Step 4: CAPA Link → If required, a CAPA is initiated directly from the NC.
Step 5: Implementation → Assigned corrective/preventive actions are carried
out.
Step 6: Verification → QA verifies and approves the effectiveness of
actions.
Step 7: Closure → NC is marked as closed.
Role-Based Responsibilities
- Initiator: Reports non-conformance incidents and provides initial details.
- Investigator: Performs RCA and documents findings and recommendations.
- Quality Manager: Reviews and approves NC details, assigns investigators, and verifies closure.
- Administrator: Defines NC categories, manages workflows, and configures permissions.
Email and Notifications
- Email notifications for NC assignments.
Security and Access Control
The module leverages the QMS’s dynamic role-based access control system to restrict actions based on user permissions. Each NC action—creation, modification, approval, or closure—is recorded in the logs to maintain transparency and compliance with audit standards.
Risk Management
The Risk Management Module in the QMS system helps organizations identify, assess, mitigate, and monitor potential risks that could affect quality, compliance, safety, or business continuity. It supports proactive risk handling in alignment with ISO 9001 and ISO 31000 standards.
Objectives
- Identify potential operational and compliance risks.
- Evaluate the likelihood and severity of identified risks.
- Develop mitigation plans and assign responsible users.
- Monitor and review risk status over time for effectiveness.
- Integrate risk management with CAPA and Audit modules for continuous improvement.
Key Features
- Risk Identification: Capture and categorize risks by department, process, or project.
- Risk Assessment: Rate each risk based on probability and impact using customizable matrices.
- Risk Prioritization: Automatically calculate risk scores and prioritize actions.
- Mitigation Planning: Assign action owners and define mitigation strategies with due dates.
- Review & Closure: Track implementation of risk mitigation actions and document outcomes.
Roles & Responsibilities
- Administrators: Configure risk categories, matrices, and scoring models; manage user access rights.
- Department Managers: Review and approve risk assessments within their departments.
- Employees: Report risks and provide updates on mitigation activities.
- Auditors / QA Team: Periodically verify risk register accuracy and evaluate effectiveness of mitigations.
Workflow Overview
Step-by-Step Flow
- Risk Identification: Users or system automatically log new risks with key details and category.
- Assessment: Each risk is evaluated for Likelihood and Impact using the risk matrix.
- Prioritization: The system calculates a risk score to classify the risk as Low, Medium, or High.
- Mitigation Planning: CAPA or corrective actions are assigned with responsibilities and deadlines.
- Review and Monitoring: Risks are monitored until closed; high-priority risks may require management review.
- Closure: Once mitigated and verified, risks are formally closed.
Benefits
- Encourages proactive identification of potential risks.
- Improves compliance readiness and operational resilience.
- Provides centralized visibility of organization-wide risks.
- Enhances decision-making through quantitative risk scoring.
- Strengthens the link between risk management and continuous improvement processes.
Complaint Management
The Complaint Management module of the Quality Management System (QMS) enables organizations to efficiently capture, manage, investigate, and resolve customer or internal complaints. This module ensures that each complaint is properly documented, analyzed, and closed with preventive or corrective actions to avoid recurrence. It promotes transparency and accountability across all stages of the complaint lifecycle.
Objectives
- Streamline the complaint handling process for timely resolutions.
- Ensure all complaints are traceable from initiation to closure.
- Enable root cause analysis and linkage to CAPA or Non-Conformance Modules.
- Generate metrics and reports for continuous improvement.
Key Features
- Complaint submission through internal or client-facing interface.
- Automatic complaint ID generation for traceability. Role-based workflow for review, investigation, and resolution.
- Ability to attach evidence, documents, and communications.
- Integration with CAPA, Non-Conformance, and Audit modules for escalations.
- Status tracking (Open, Under Review, In Progress, Resolved, Closed).
Workflow
- Complaint Initiation: A user (employee or client) submits a new complaint via the complaint form or client portal.
- Review & Assignment: The Quality Manager or designated role reviews the complaint and assigns it to the responsible department.
- Investigation: The assigned department investigates the root cause, attaches findings, and suggests corrective actions if needed.
- CAPA Linking: If the issue requires corrective or preventive action, a CAPA record is created and linked.
- Resolution & Approval: The responsible authority reviews investigation results and approves resolution steps.
- Closure: Once verified and approved, the complaint is closed and archived for audit purposes.
Role-Based Responsibilities
| Role | Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Administrator | Configure complaint types and assign permissions. |
| Quality Manager | Review complaints, assign investigations, and ensure timely resolution. |
| Investigator / Department Head | Conduct investigation, identify root cause, and propose corrective actions. |
| Employee / Client | Submit complaint, provide evidence, and track status updates. |
Email & Notifications
- Automatic email notifications upon new complaint submission.
Security & Access Control
The Complaint Module adheres to dynamic role-based access control (RBAC). Each role has predefined permissions to ensure secure handling of sensitive complaint data. Access is controlled based on user roles, complaint ownership, and organizational hierarchy.
Benefits
- Centralized complaint management system ensuring accountability.
- Enhanced transparency across investigation and resolution processes.
- Reduced recurrence of similar complaints through CAPA integration.
- Improved customer satisfaction and regulatory compliance.
Training Module
The Employee Training Module is designed to manage and monitor all training activities within the Quality Management System (QMS). It helps ensure that employees are properly trained and qualified for their roles, and that all training records are centrally managed and auditable. The module automates training assignments, reminders, and compliance tracking.
Objectives
- Streamline the process of assigning and tracking employee training programs.
- Ensure employee competency through structured and recorded training sessions.
- Provide evidence of training completion for audits and compliance.
- Automate reminders for upcoming or overdue training sessions.
Key Features
- Creation and management of training programs, courses, and sessions.
- Employee-wise and role-based training assignment.
- Online and offline training tracking (e-learning, workshops, certifications).
- Automatic reminders and notifications for scheduled training.
- Integration with Document Management for storing training materials.
- Certificate generation upon completion of mandatory courses.
Workflow
- Training Program Setup: The HR or Quality Manager creates a training program defining objectives, content, and applicable roles or departments.
- Employee Assignment: Employees are automatically or manually assigned to relevant training programs based on their role or department.
- Training Execution: Employees complete the training either online or in-person. Supporting materials (videos, documents) are made available via the system.
- Assessment & Feedback: Optional assessments or quizzes can be conducted to measure understanding and effectiveness.
- Completion & Certification: Once the training is completed and verified, a digital certificate is generated.
- Tracking & Reporting: The system maintains records of completion and provides reports to management and auditors.
Role-Based Responsibilities
| Role | Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Administrator | Configure training permissions, and manage access control. |
| HR / Quality Manager | Create and assign training programs, review completion status, and approve certificates. |
| Trainer / Instructor | Deliver training content, record attendance, and evaluate employee performance. |
| Employee | Complete assigned training and submit feedback or assessments as required. |
Email & Notifications
- Email notifications for new training assignments.
Benefits
- Centralized management of employee training records and materials.
- Enhanced compliance with ISO and regulatory training requirements.
- Improved employee competency tracking and audit readiness.
Document Management System
The Document Management Module in the QMS system provides a centralized and secure environment for managing all organizational documents related to quality management. It ensures document traceability, compliance, and collaboration through features like AI-assisted document handling, cloud integration, and digital signatures. The module supports document versioning, structured storage, and audit trails to maintain accountability and transparency across all document workflows.
Key Features
1. Smart Document Organization
Documents are automatically categorized and stored under logical folders based on metadata such as document type, department, or project. The system allows users to tag, filter, and retrieve files efficiently, promoting structured content management.
2. OCR-Based Deep Search
Integrated OCR technology converts scanned images and PDFs into searchable text, enabling users to perform deep keyword-based searches across document content. This feature improves accessibility and retrieval time for critical files.
3. AI-Based Document Generation & Summarization
The system leverages AI to assist in generating reports, summaries, and templates automatically. It helps users quickly understand lengthy documents through AI-powered summarization, ensuring faster decision-making and compliance reviews.
4. Secure Document Sharing
Users can share documents securely within or outside the organization using access-controlled, encrypted links. Permissions can be defined to restrict downloading, editing, or forwarding, maintaining data confidentiality.
5. Cloud Storage Integration
The module integrates seamlessly with popular cloud storage providers such as AWS S3, Google Drive, or Azure Blob Storage. This ensures scalable storage capacity and reliable backup for all managed documents.
6. Share Documents via Encrypted Links
Enables users to send documents externally through secure, encrypted URLs that can be time-bound or password-protected. This feature ensures controlled external collaboration without compromising security.
7. Document Version Control
Every document revision is automatically versioned, maintaining a clear history of changes. Users can review previous versions, track modifications, and restore earlier iterations if necessary.
8. Document Archiving with Retention
Supports automated archiving of outdated or inactive documents based on retention policies. Archived documents remain accessible for audit or compliance purposes while keeping active storage optimized.
9. Document Signature
Integrated digital signature functionality allows users to sign documents electronically. Signatures are timestamped, legally compliant, and verifiable for document authenticity.
10. Detailed Audit Trails for Every Document
Each document action—upload, view, edit, share, delete—is logged for traceability. Administrators can view audit trails to ensure accountability and compliance with regulatory standards.
11. Built-In Document Preview
Users can preview documents (PDFs, Word, Excel, images) directly in the browser without downloading. This promotes convenience and minimizes data exposure risks.
12. Request Documents via Secure Links
Enables users or administrators to request specific documents from internal teams or external partners through secure upload links. Uploaded files are automatically categorized and tracked within the system.
Workflow Automation
The Workflow Automation module streamlines and automates document-related processes to enhance operational efficiency, minimize manual intervention, and ensure standardized handling across your organization. It empowers users to define custom workflows for tasks such as approvals, reviews, status changes, and notifications—all triggered automatically based on predefined rules or user actions.
- Create custom workflows tailored to document lifecycle and business needs.
- Automate tasks like approval routing, status updates, and notifications.
- Track real-time progress and monitor workflow status at every step.
- Reduce delays and ensure timely completion of assigned steps.
- Enforce compliance with standard operating procedures and internal policies.
Core Functions
1. Workflow Creation
Users can create workflows using an intuitive interface where they define each stage (e.g., Draft, Review, Approval, Finalization). Each stage includes associated actions, responsible users, and automated triggers.
2. Task Automation
Tasks such as sending approval requests, changing document statuses, or sending reminder emails can be fully automated. These triggers reduce manual workload and ensure consistent process adherence.
3. Real-Time Workflow Tracking
Every workflow has a live status tracker that displays its current stage, assigned user, and pending actions. Users can monitor progress through dashboards or detailed status views.
5. Notifications and Alerts
Automated in-system alerts are triggered whenever a workflow progresses to the next stage, keeping stakeholders informed in real time.
6. Workflow Templates
Frequently used processes (e.g., Document Review or Supplier Approval) can be saved as templates, allowing quick reuse for similar operations and maintaining process uniformity.
Sample Workflow Example
Example: Document Approval Workflow
- Step 1: Draft Creation – A user uploads or creates a new document in the Document Management module.
- Step 2: Review Stage – The document is automatically assigned to reviewers based on department or project type.
- Step 3: Feedback and Revision – Reviewers provide comments; the document returns to the author for edits if required.
- Step 4: Approval – Once revisions are complete, the document routes to the approver for final authorization.
- Step 5: Finalization – After approval, the document status automatically updates to “Approved” and notifies relevant team members.
- Step 6: Archiving and Audit – The approved document is versioned and archived automatically, with a full audit trail logged for compliance.
Role Responsibilities
- Workflow Creator: Defines workflow stages, rules, and responsible roles.
- Reviewer: Reviews, comments, and provides feedback on assigned items.
- Approver: Finalizes the process by approving or rejecting workflow items.
- Administrator: Manages templates, monitors system-level workflow performance, and sets permissions.
Workflow Relationship Diagram (Textual Representation)
[Draft Created] → [Review Stage] → [Approval Stage] → [Finalization] → [Archiving]
| | | |
↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
(Author) (Reviewer) (Approver) (System Archive)
Automated Reminder & Notification Scheduler
The Automated Reminder & Notification Scheduler is an intelligent scheduling engine integrated within the Document Management System to ensure that no critical task, review, or document deadline is ever missed. This feature enables users to configure custom reminders for both document-specific and system-wide activities, helping teams maintain compliance, improve responsiveness, and streamline operations.
With this module, administrators and users can define recurring or one-time reminders, customize alert frequency, and ensure targeted notifications reach the right personnel—enhancing transparency and efficiency throughout the document lifecycle.
Core Features
- Recurring Reminders: Schedule reminders at multiple intervals including Daily, Weekly, Monthly, Quarterly, Half-Yearly, Yearly, or for a Specific Date—perfect for document renewals, policy updates, or audit cycles.
- System-Level & Document-Level Scheduling: Create reminders that apply globally across the system (for shared compliance events) or specific to individual documents (such as contract expirations or review deadlines).
- Smart Notifications & Alerts: Automatically send real-time notifications and email alerts to designated users or groups when a reminder is triggered, ensuring critical deadlines are never missed.
- User-Specific Triggers: Configure alerts based on user roles and responsibilities. For example, compliance officers can receive policy renewal reminders, while document owners get notified of review cycles.
- Flexible Delivery Options: Deliver reminders through multiple channels such as email, in-app alerts, or dashboard widgets to suit each user’s workflow preferences.
- Integration with Workflow Module: Seamlessly link reminders with automated workflows to trigger subsequent actions—like initiating approvals or escalating overdue tasks.
- Audit Logging: Every sent notification and triggered reminder is logged for full traceability, ensuring compliance and accountability.
Sample Example
A Compliance Document is set to expire on March 31, 2026. The system automatically schedules reminders for:
- 30 days before expiration (to the Document Owner and Compliance Officer)
- 7 days before expiration (to the Department Head)
- On the expiration date (system-wide alert for archival or renewal)
If the document is not renewed by the expiration date, the system automatically marks it for archiving and notifies the responsible department for follow-up.
Role Responsibilities
- Administrator: Defines global reminder templates, sets organization-wide alert policies, and reviews audit logs of sent notifications.
- Document Owner: Configures document-specific reminders for renewals, approvals, or mandatory reviews.
- Department Head: Receives escalations for overdue tasks or documents awaiting approval.
- Employee/User: Receives task-specific reminders related to assigned responsibilities.
Notification Lifecycle
- 1. Reminder Creation: User defines a reminder (recurrence type, recipients, and delivery method).
- 2. Scheduler Activation: The system automatically monitors upcoming events using background scheduling.
- 3. Notification Trigger: When due, the system sends notifications through the chosen channels.
- 4. User Acknowledgement: Recipients acknowledge or act upon the reminder (e.g., renew, approve, or upload a document).
- 5. Audit Logging: Every action and reminder event is recorded for compliance tracking.
Rate Us on CodeCanyon
We hope this documentation has helped you successfully set up and use the Quality Management System System. If you’ve found this product valuable, please consider showing your support by leaving a 5-star rating on CodeCanyon. ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
Your positive feedback not only motivates us to keep improving but also helps other users make confident decisions.
If you encounter any issues or need assistance, feel free to reach out through our support portal. We’re here to help!